Collections
-
Stack, LinkedList, Queue
- -
What we’ll cover
What is a Stack?
The Stack Interface
Stack Methods
LinkedList
The Queue Interface
Queue Methods
-
Stack

-
What is a Stack?
- Models a real-life stack.
- Gives client access to a
Stackwith only the top-most card accessible.- LIFO
- Insertions can only be to the top of the
Stack- The indices of other elements in the stack are shifted up 1.
- Removals can only be from the top of the
Stack- The indices of other elements in the stack are shifted down 1.
-
Shortcomings of Java’s Stack class
- Should have been interface
- Stack is a subclass of
Vectoris a subclass ofAbstractList- client has ability to insert into/remove from anywhere in the stack.
- violates the nature of a stack
-
Stack methods
- pop()
- push()
- peek()
- isEmpty()
-
isEmpty()
- returns true if
Stackcontains no elements
-
isEmpty() example
@Test
public void demo() {
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
System.out.println(stack.isEmpty()); // prints true
}
Output
true
-
push()
- populates the
Stackwith the respective argument - newly inserted element is considered to be the
heador top-of-stack
-
push() example
@Test
public void demo() {
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push("Hello world");
System.out.println(stack.isEmpty()); // prints false
}
Output
false
-
peek()
- views the most recently added item
-
peek() example
@Test
public void demo() {
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push("Hello world");
System.out.println(stack.peek());
}
Output
Hello world
-
pop()
- removes and returns the most recently added element
-
pop() example
@Test
public void demo() {
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
System.out.println(stack.isEmpty()); // prints true
stack.push("Hello world");
System.out.println(stack.isEmpty()); // prints false
String topValue = stack.pop();
System.out.println(topValue); //prints "Hello World"
String topValue2 = stack.pop(); // throws EmptyStackException
}
Output
true
false
Hello world
java.util.EmptyStackException
at java.base/java.util.Stack.peek(Stack.java:102)
-
Stack Methods
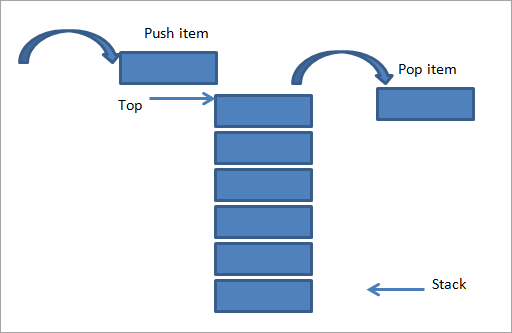
-
LinkedList
LinkedListis quicker thanArrayListat removal/insertion of elements in the middle of the list.LinkedListvalues are stored asNodeobjects.- Each
Nodeis a separate object with adataandnextfield.
- Each
-
Node
class Node<DataType> {
DataType data;
Node next;
Node(DataType d) {
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
-
LinkedList
class LinkedList<DataType> {
Node<DataType> head;
}
-
LinkedList
- Iterating a linked list:
- Requires client to continually check if
nextis null, if notthis.head = next
- Requires client to continually check if
-
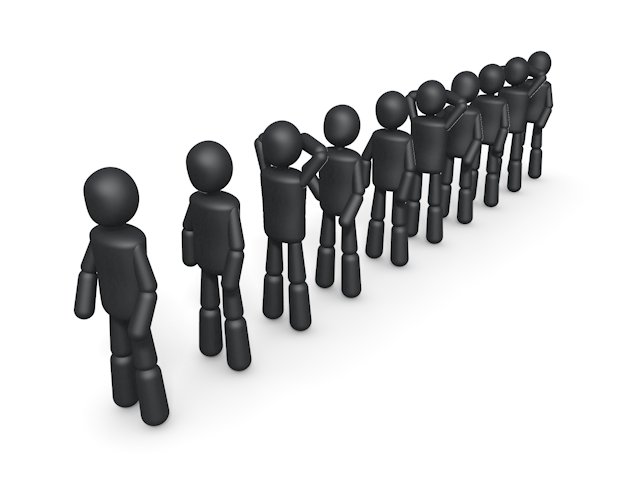
Queue Interface
- Specifies that you can
- add elements at the tail end of the queue,
- remove elements at the head,
- find out how many elements are in the queue.
- FIFO implementation
-
Queue Interface

-
Minimal Form of a Queue Interface
- The interface describes the intent without detailing the implementation
// a simplified form of the interface in the standard library
public interface Queue<E> {
void add(E element);
E remove();
E peek();
int size();
}
-
Queue API Structure
- There are 3 primary types of Queue-Operations
- Adding:
add(e)/offer(e) - Removing:
remove()/poll() - Viewing:
element()/peek()
- Adding:
-
Queue API Structure: Adding
-
Queue API Structure
add(e)
- Adds an element to the tail of the Queue.
- Has potential to throw
IllegalStateExceptionIllegalStateExceptionif the element cannot be added at this time due to capacity restrictionsClassCastExceptionif the class of the specified element prevents it from being added to this queueNullPointerExceptionif the specified element is null and this queue does not permit null elementsIllegalArgumentExceptionif some property of this element prevents it from being added to this queue
-
Queue API Structure
offer(e)
- Adds an element to the tail of the Queue.
- Does not have potential to throw
IllegalStateExceptionClassCastExceptionif the class of the specified element prevents it from being added to this queueNullPointerExceptionif the specified element is null and this queue does not permit null elementsIllegalArgumentExceptionif some property of this element prevents it from being added to this queue
-
Queue API Structure: Removing
-
Queue API Structure
remove()
- Removes element at the head of the Queue.
- Has potential to throw an exception.
NoSuchElementExceptionif this queue is empty
-
Queue API Structure
poll()
- Removes element at the head of the Queue.
- Throws no exceptions
-
Queue API Structure: Viewing
-
Queue API Structure
element()
- Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of the queue.
- Has the potential to throw an exception
NoSuchElementExceptionif this queue is empty
-
Queue API Structure
peek()
- Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of the queue.
- Throws no exceptions
-
Queues, Deques, and Stacks
- Queue – Adds elements to one end and removes from the other (FIFO)
- Stack – Adds elements to one end and removes them from the same (LIFO)
- Deque – “double-ended queue” adds and removes elements at both ends
Note: Deque is often used for stacks as well
-
All About Queues
- Read more here
-
